
Sixty percent of future enterprise 5G rollouts are expected to happen within a building, according to Omdia research. With 5G, the building becomes both a source and a location for value creation, not just where the bulk of network traffic happens to transit.
Pressure to reinvent is acute after COVID-19: owners and managers of major property assets must work harder to entice tenants, fans, and visitors to return.
 Places of mass interaction such as offices, stores, ports, and stadiums must be attractive, safe, useful, and operationally efficient.
Places of mass interaction such as offices, stores, ports, and stadiums must be attractive, safe, useful, and operationally efficient.
While building automation is itself a growing market, 5G brings opportunities to create value in completely different ways for a wide range of beneficiaries.
Through 5G, spaces can become smarter and faster, not only by providing real-time and predictive insights on how people and things behave within an environment but also by enabling new interactions and collaborations such as personalized real-time video, digital signage, or location intelligence.
Communication service providers (CSPs) can play a huge role if they stop thinking of the building as a formal demarcation point between the services that they offer and what other suppliers provide. Leveraging 5G, the CSP can play a role in smart spaces that is collaborative beyond physical walls.
A smart space can exist across one or several buildings but encompasses much more than automating building management functions and connecting sensors or enabling broadband access. Implemented correctly, a smart space becomes a service platform and can share in the network effects as its supplier and user community grows.
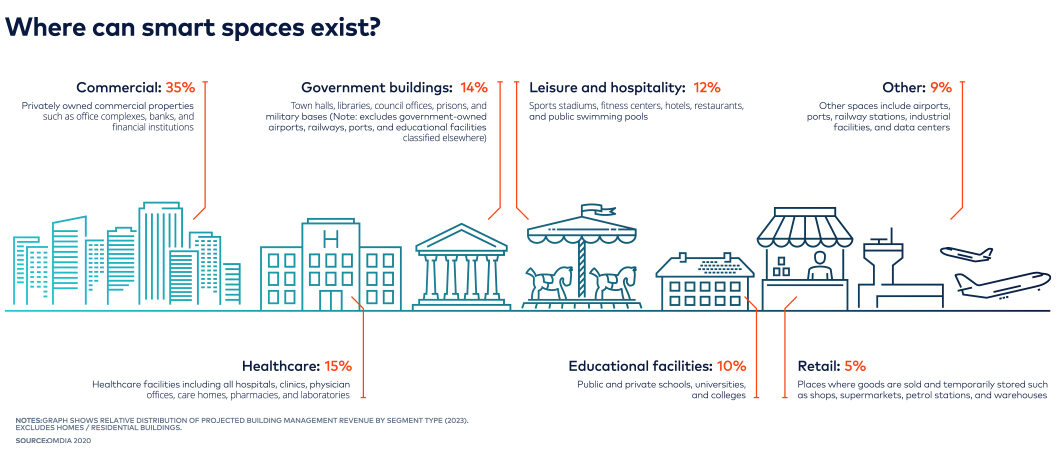
Various segments of the built environment can become smart. In recent years, the fastest-growing segments for building technology investment have been healthcare, leisure, and hospitality facilities.
Already, many enterprises want to deliver insights and new applications across domains. Examples include blending the building environment with workforce tools to enable better productivity and using operational monitoring such as camera infrastructure to create premium services.
Central to these aims is harvesting and combining intelligence from various sources to make decisions, protect, educate, and even entertain. Building operations data (such as light, temperature, and power consumption) is only a starting point. Trend analysis can help suggest better decisions to reduce energy usage, improve environmental comfort, and reduce safety risks. But it could also suggest new services by analyzing a tenant's daily working habits.
But even with smart building technology in place, many enterprises do not routinely analyze their building data or combine it with non-building data in creative ways.
They need help to act on their stated priorities.
To become really smart, spaces should be able to adapt to new needs on the fly. CSPs working with technology partners and other experts can remove boundaries between knowledge silos inside and outside the enterprise.
Beyond Now worked in collaboration with Omdia to create an eBook exploring the value that 5G can bring to smart spaces, including analysis and case studies.

